M^3 (Making Math Meaningful) Cofunction Angle Identities
Cofunction Formulas, also known as Cofunction Identities, are a set of trigonometric identities that establish relationships between the trigonometric functions of complementary angles. Complementary angles are two angles whose sum is equal to \(90\) degrees (\(\frac{\pi}{2}\) radians), forming a right angle.
M^3 (Making Math Meaningful) Cofunction Angle Identities
Trigonometric co-function identities are relationships between the basic trigonometric functions (sine and cosine) based on complementary angles. They also show that the graphs of sine and cosine are identical, but shifted by a constant of \ (\frac {\pi} {2}\).

CoFunction Identity Thinking Application YouTube
cos = sin Pythagorean Identities Consider a point on the unit circle: 6 y P(x; y) = (cos ; sin ) x = tan 1 = cot which leads to triangle 1 sin cos Using the Pythagorean theorem, we see that (memorize this one): cos2 + sin2 = 1 Derive two other identities from the one we have memorized: Divide by cos2 : cos2 cos2 sin2
Cofunction Identities YouTube
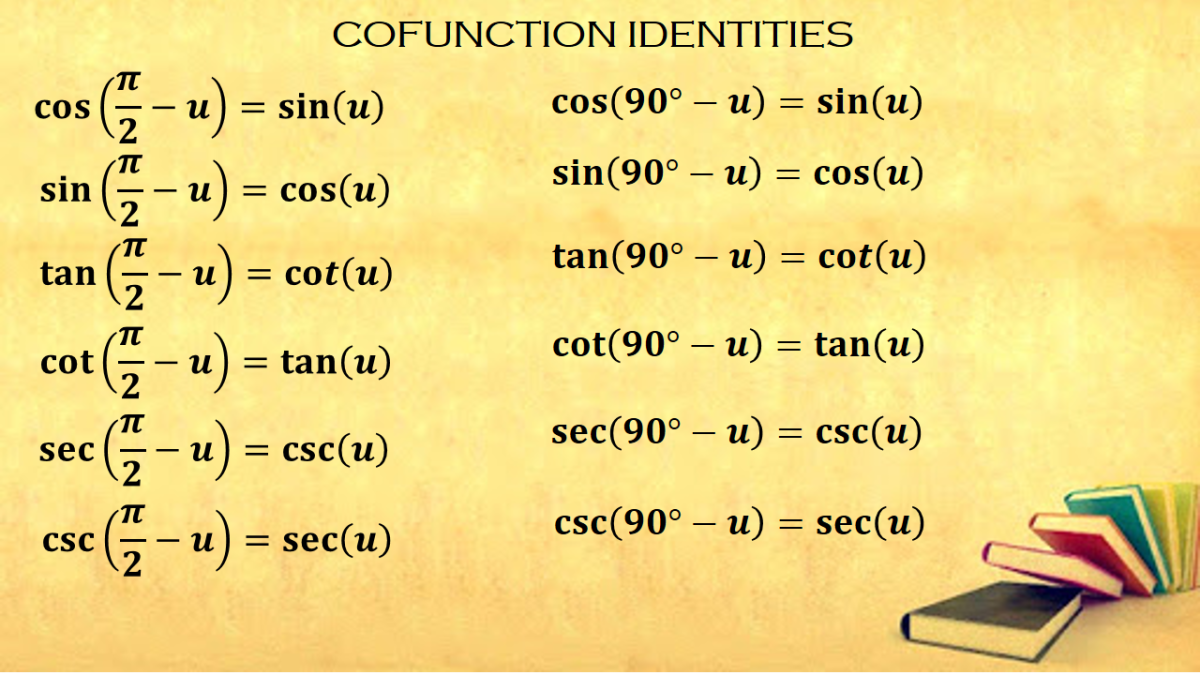
The cofunction identities are summarized in Table 7.2.2. Table 7.2.2. sinθ = cos(π 2 − θ) cosθ = sin(π 2 − θ) tanθ = cot(π 2 − θ) cotθ = tan(π 2 − θ) secθ = csc(π 2 − θ) cscθ = sec(π 2 − θ) Notice that the formulas in the table may also justified algebraically using the sum and difference formulas.
Cofunction Identities in Trigonometry (With Proof and Examples) Owlcation
The cofunction identities establish a relationship between trigonometric functions \ (sin\) and \ (cos\), \ (tan\) and \ (cot\), and \ (sec\) and \ (csc\). These functions are known as cofunctions of each other. We can write cofunction identities in terms of radians and degrees because these are the units of angle measurement.

Cofunction Identities in Trigonometry (With Proof and Examples) Owlcation
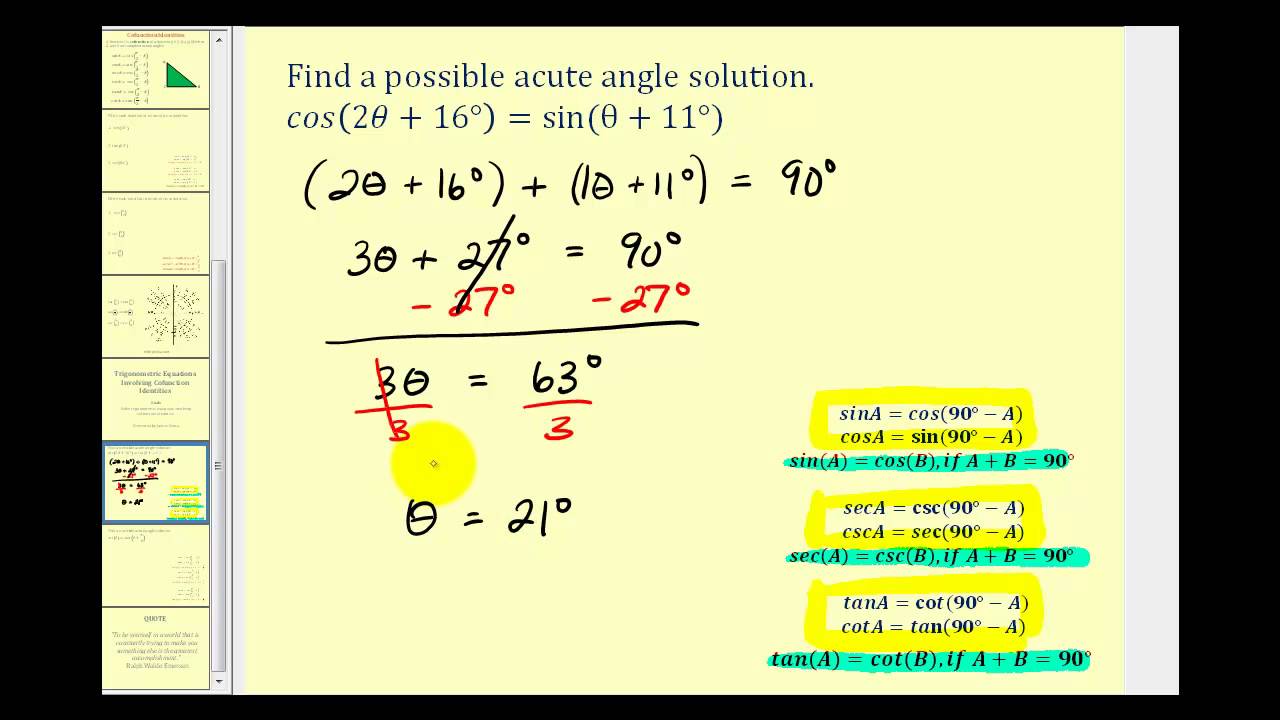
What are the Co-function Identities? A function f is cofunction of a function g if f (A) = g (B) when A and B are complementary angles. sin A = cos (90° - A) cos A = sin (90° - A) sin A = cos B, if A + B = 90° sec A = csc (90° - A) csc A = sec (90° - A) sec A = csc B, if A + B = 90° tan A = cot (90° - A) cot A = tan (90° - A)

Cofunctions Definition & Examples Video & Lesson Transcript
The cofunction identities For example: Given that the the complement of Radians Sine and co sine are co functions and complements Tangent and co tangent are co functions and complements Secant and co secant are co functions and complements Degree Sine and co sine are cofunctions and complements sin (90° - x) = cos x cos (90° - x) = sin x
Cofunction Identities Examples & Practice Problems Trigonometry YouTube
So, what does that mean? Show Answer Most Common Cofunction Formulas sine and cosine Degree example sin(θ) = cos(90 − θ) s i n ( θ) = c o s ( 90 − θ) cos(θ) = sin(90 − θ) c o s ( θ) = s i n ( 90 − θ) Radian example sin(θ) = cos(π2 − θ) s i n ( θ) = c o s ( π 2 − θ) cos(θ) = sin(π2 − θ) c o s ( θ) = s i n ( π 2 − θ) tangent and cotangent

Cofunction Identities Trigonometry Trigonometry, Math tutor, Email
What are Cofunction Identities? A function f is cofunction of a function g if f(A) = g(B) when A and B are complementary angles. sin(A) = cos(B), if A + B = 90° sec(A) = scs(B), if A + B = 90° tan(A) = cot(B), if A + B = 90° The following figures give the cofunction identities. Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions on how to.
Cofunction Identities in Trigonometry (With Proof and Examples) Owlcation
The cofunction identities show the relationship between sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, secant, and cosecant. The value of an angle's trig function equals the value of the angle's complement's cofunction. We refer to the sine and cosine functions as cofunctions of each other.

CoRelated CoFunction Trigonometric Identities Concepts Part 1 YouTube
The cofunction identity for sine can be expressed as the mathematical equation sin (theta) = cos (pi/2-theta). What is the cofunction of CSC? CSC is an abbreviation for the trig function.

Cofunction Identities in Trigonometry (With Proof and Examples) Owlcation
The Cofunction and Odd-Even Identities The Cofunction Identities sin ( π 2 − x ) = cos ( x ) cos ( π 2 − x ). Example: Find the value of cot ( 60 ° ) . Use the co-function identity.

Precalc Cofunction identities & odd even YouTube
Cofunction Identities Examples & Practice Problems. The Organic Chemistry Tutor. 199. 03:55. Cofunction Identities (Trigonometry) - Understanding Them. Mario's Math Tutoring. 126. 07:07. Using your trig and co function identities to evaluate. Brian McLogan. 89. 02:36. Cofunction Identities, Example 2. patrickJMT. 100.
Cofunction Identities in Trigonometry (With Proof and Examples) Owlcation
Cofunction identities are trigonometric identities that show the relationship between trigonometric ratios pairwise (sine and cosine, tangent and cotangent, secant and cosecant). We use the angle sum property of a triangle to derive the six cofunction identities.
Cofunction Identities Solving Trigonometric Equations YouTube
Cofunction Identities Examples & Practice Problems. The Organic Chemistry Tutor. 625. 03:55. Cofunction Identities (Trigonometry) - Understanding Them. Mario's Math Tutoring. 230. 07:07. Using your trig and co function identities to evaluate. Brian McLogan. 212. 02:36. Cofunction Identities, Example 2. patrickJMT. 429.

Cofunction Formulas Trigonometric Identities & Solved Examples
cofunction: Cofunctions are functions that are identical except for a reflection and horizontal shift. Examples include: sine and cosine, tangent and cotangent, secant and cosecant. even: An even function is a function with a graph that is symmetric with respect to the y-axis and has the property that \(f(−x)=f(x)\). identity