Ear infections explained Dr Mark McGrath
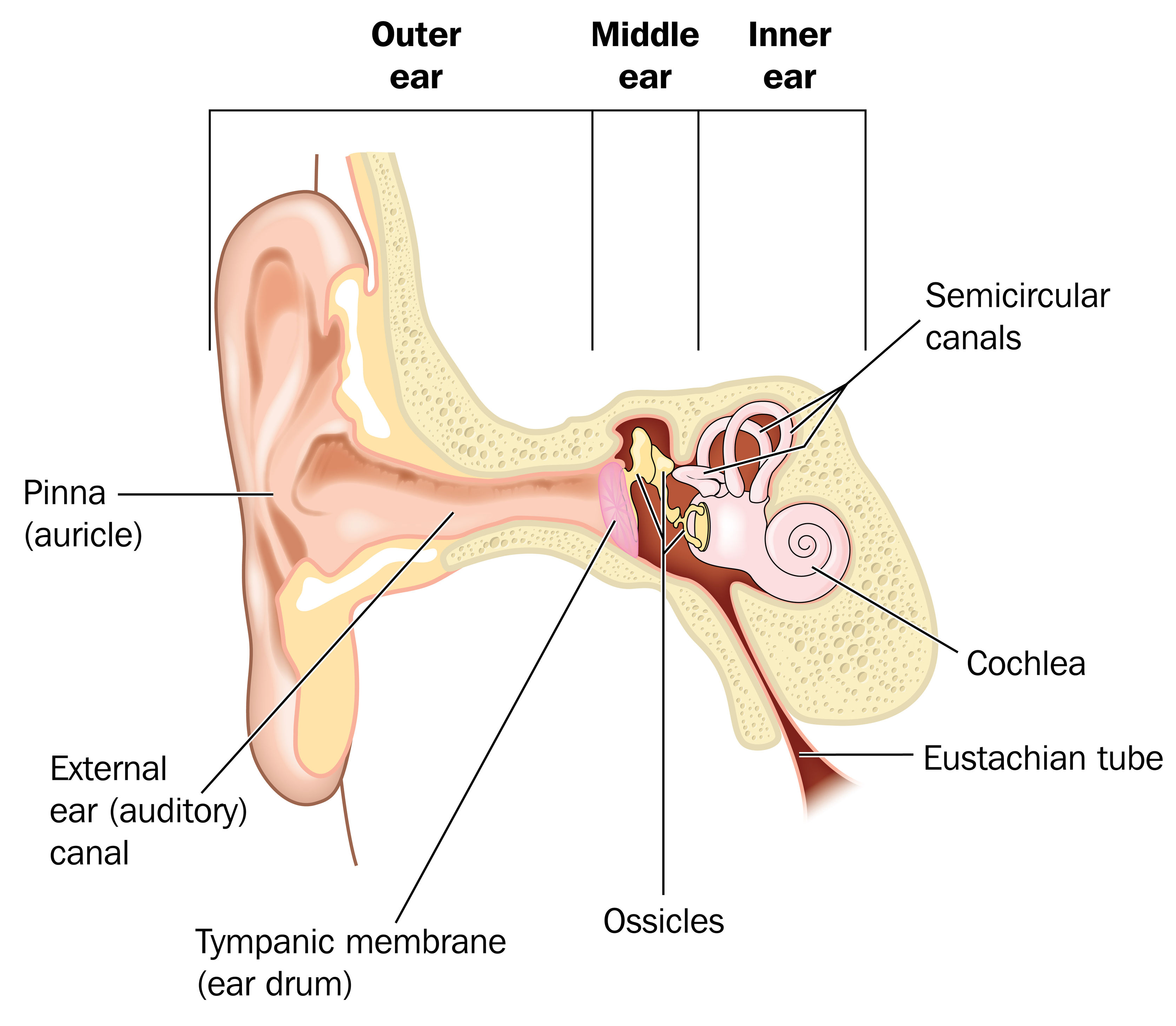
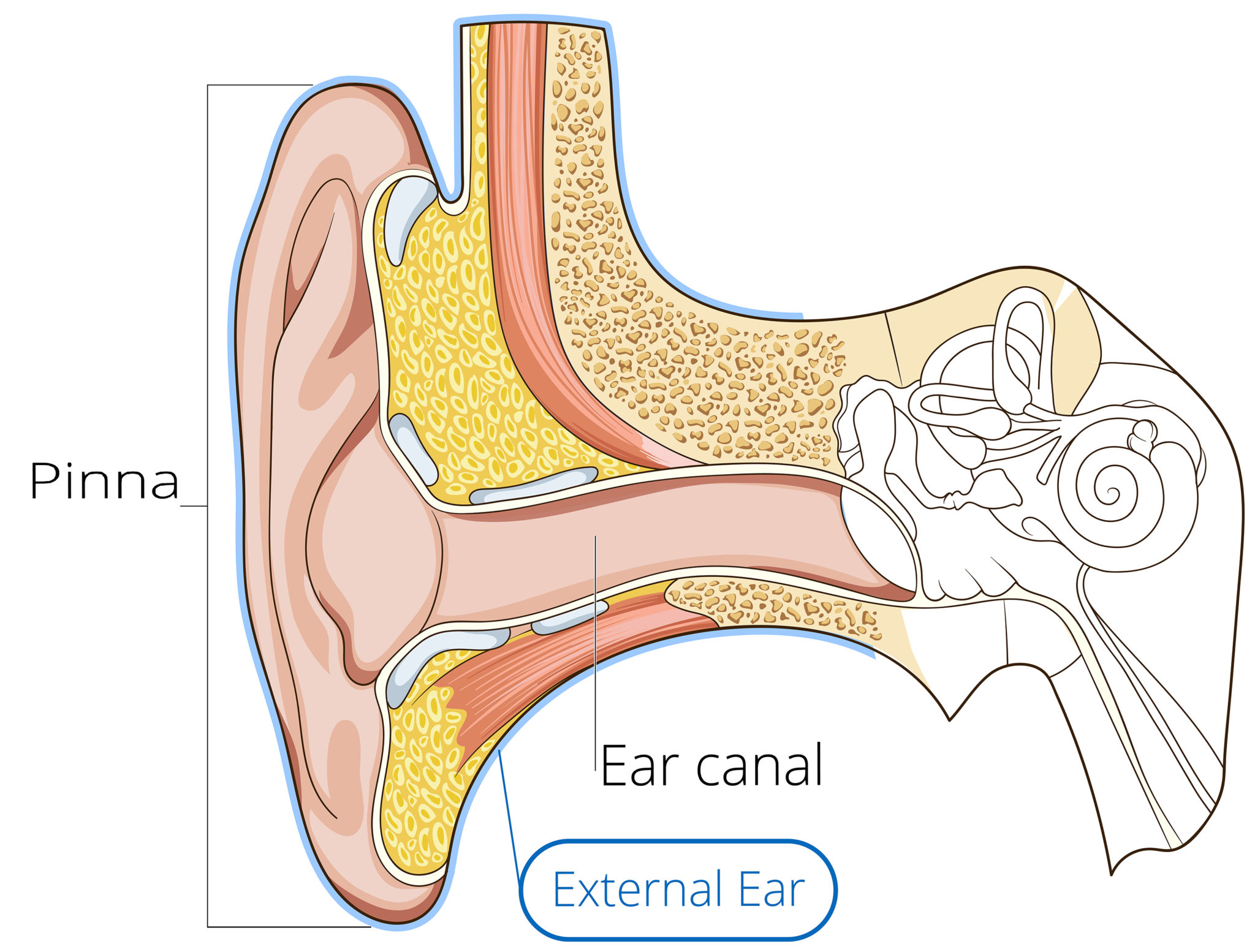
1/4 Synonyms: External auditory meatus, External acoustic pore , show more. The ear is a complex part of an even more complex sensory system. It is situated bilaterally on the human skull, at the same level as the nose. The main functions of the ear are, of course, hearing, as well as constantly maintaining balance.

EarQ Anatomy of the Ear Chart Human ear, Inner ear diagram, Ear anatomy
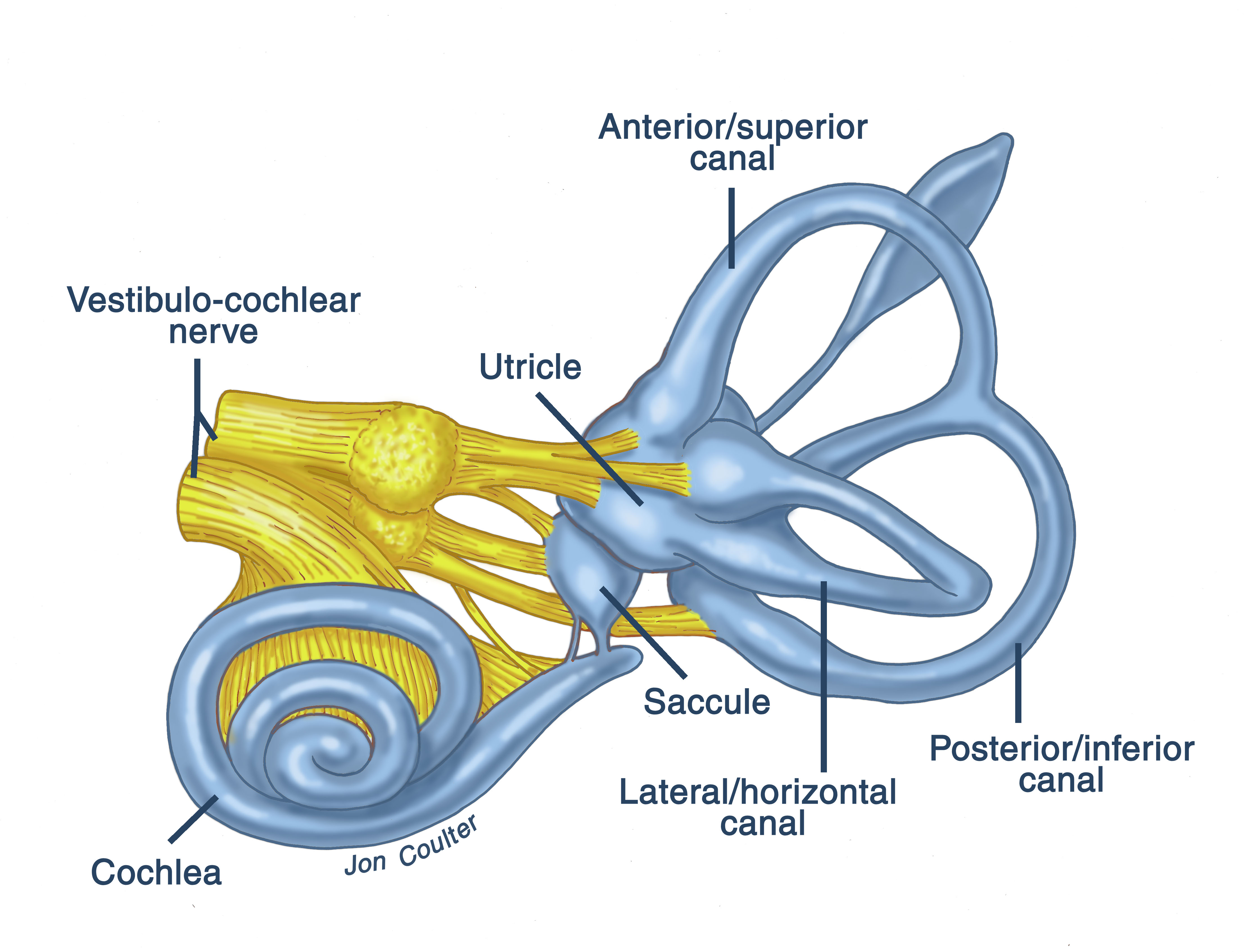
Anatomy. The inner ear is a complex three dimensional shape with semicircular canals, dilations called the utricle and saccule and a spiral portion known as the cochlea. All of these organs are housed inside a bony shell known as the bony labyrinth and this is within the temporal bone. The cochlea is the site where sound is transformed into.

Ear Anatomy Vestibular Disorders Association
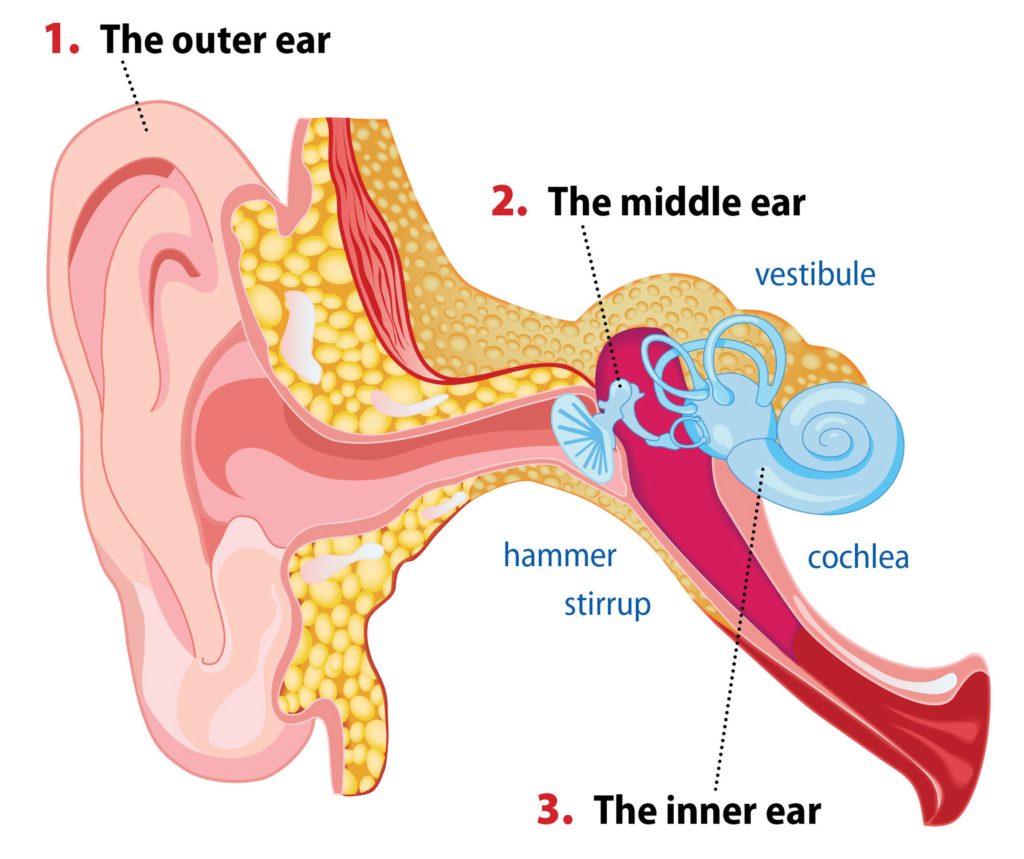
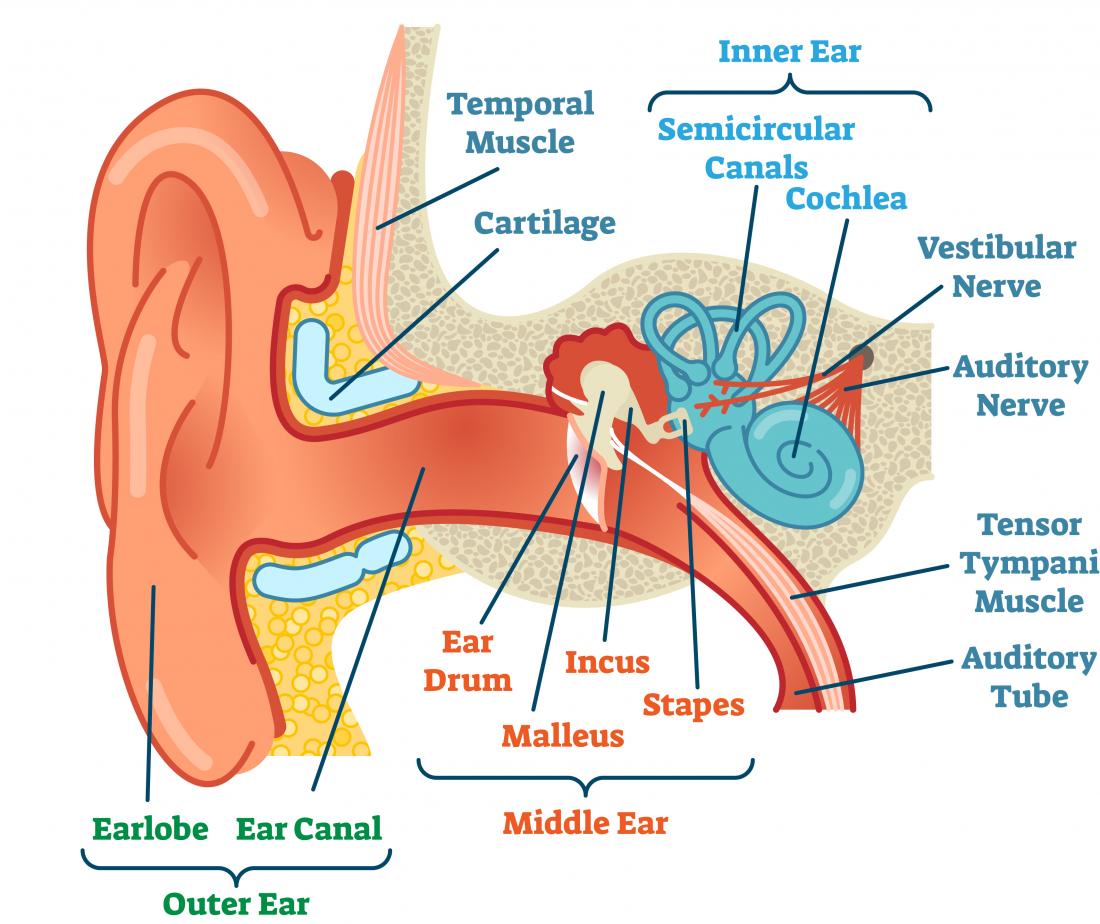
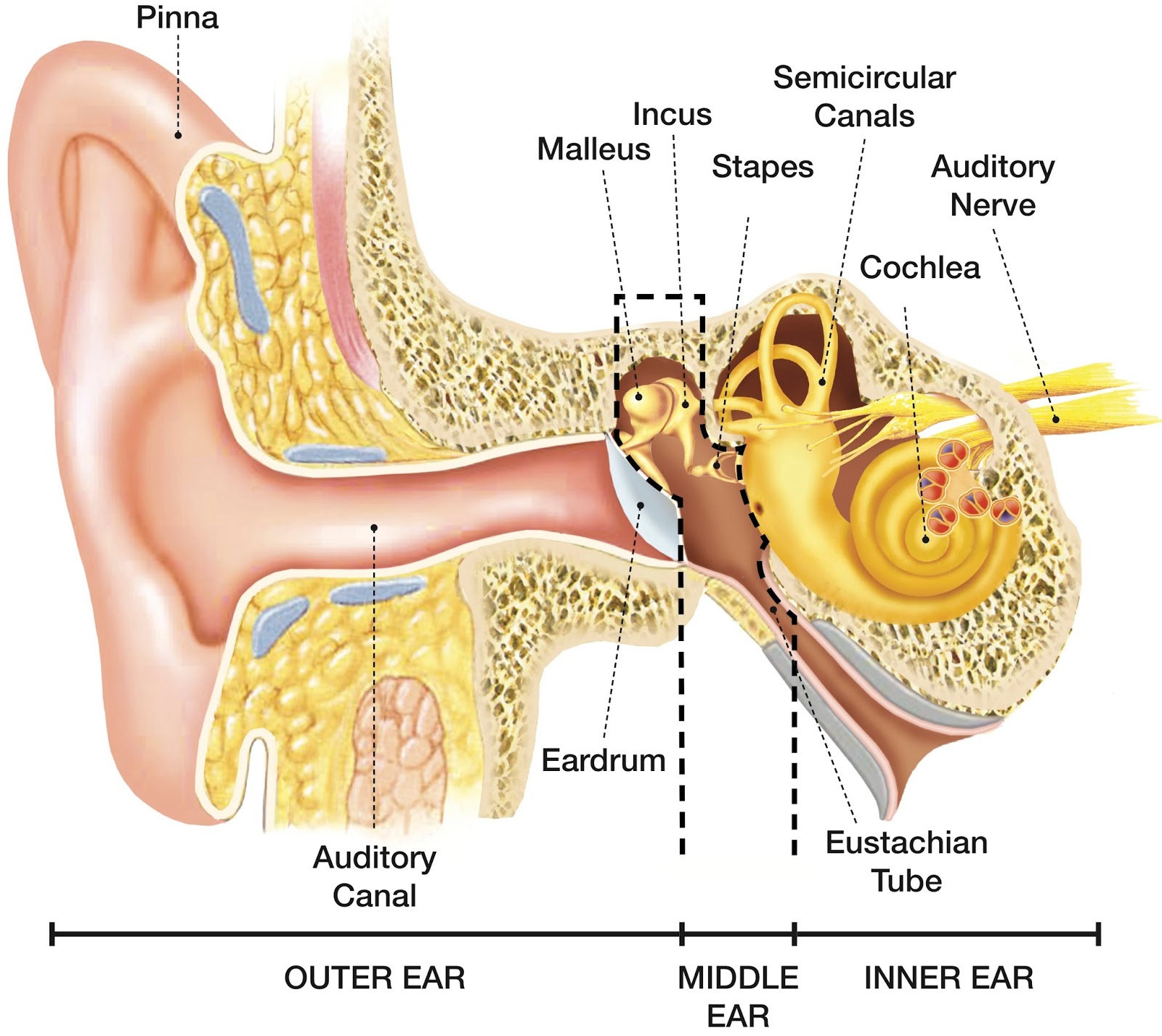
Structure and Function. The ear is organized into three different anatomical structures: the outer, middle, and inner ear. The outer ear consists of the pinna, external auditory canal, and tympanic membrane and is responsible for the transmission of sound waves from the external environment. The middle ear is an air-filled space that contains the three ossicles (malleus, incus, and stapes.
How does your ear work?
Sound waves are created when air vibrates. To hear, the ear needs to change sound into electrical signals which the brain can interpret. The outer part of the ear (the pinna) funnels sound waves into the ear canal. When sound waves reach the eardrum they cause it to vibrate. Vibrations of the eardrum cause the tiny bones in the middle ear to.

Inner Ear Problems Causes & Treatment of inner ear Dizziness & Vertigo
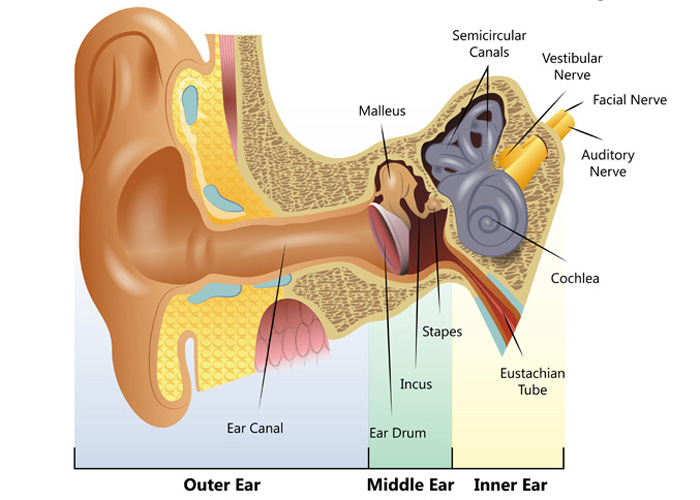
Balance: Your inner ear contains semicircular canals filled with fluid and hair-like sensors. When you move your head, the fluid inside these loop-shaped canals sloshes around and moves the hairs. The hairs transmit this information along the vestibular nerve to your brain.
Ear Anatomy Causes of Hearing Loss Hearing Aids Audiology
The hearing part of the inner ear is called the cochlea. This comes from the Greek word for 'snail' because of its distinctive coiled shape. The cochlea, which contains many thousands of sensory cells (called 'hair cells'), is connected to the central hearing system by the hearing or auditory nerve.
What is conductive hearing loss? Blog of Kiversal
Chapter 1 - Introduction Manual Format How to examine the ears Suggested Procedure Chapter 2 - Testing Audiogram Tympanogram Chapter 3 - Ear Anatomy Ear Anatomy - Outer Ear Ear Anatomy - Inner Ear Ear Anatomy Schematics Ear Anatomy Images Chapter 4 - Fluid in the ear Fluid in the ear Discussion Fluid in the ear Outline Middle Ear Ventilation Tubes
How The Ear Works Step by Step Brief Explanation
Click Image to Enlarge. The ear is the organ of hearing and balance. The parts of the ear include: External or outer ear, consisting of: Pinna or auricle. This is the outside part of the ear. External auditory canal or tube. This is the tube that connects the outer ear to the inside or middle ear. Tympanic membrane (eardrum).

Medical problems of the eyes, ears, nose, and throat symptoms
Structure The ear is made up of the outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear. The inner ear consists of the bony labyrinth and membranous labyrinth. The bony labyrinth comprises three components: Cochlea: The cochlea is made of a hollow bone shaped like a snail and divided into two chambers by a membrane.

Afbeeldingsresultaat voor middle ear anatomy Ear anatomy, Middle ear
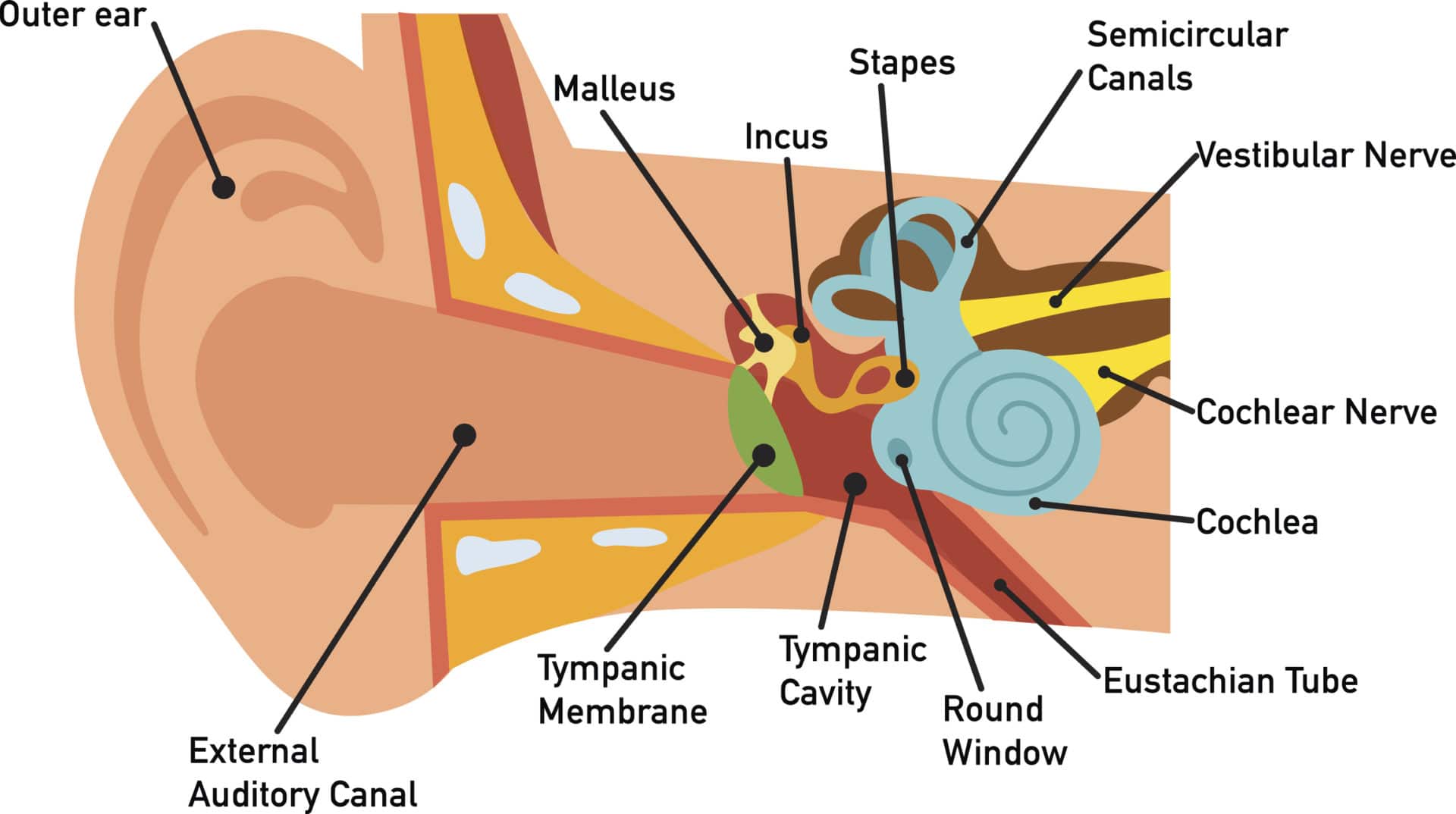
The inner ear has two openings into the middle ear, both covered by membranes. The oval window lies between the middle ear and the vestibule, whilst the round window separates the middle ear from the scala tympani (part of the cochlear duct). Bony Labyrinth. The bony labyrinth is a series of bony cavities within the petrous part of the temporal.
How You Hear Northland Audiology
Inner ear anatomy. The outer, middle, and inner ear. The inner ear is at the end of the ear tubes. It sits in a small hole-like cavity in the skull bones on both sides of the head. The inner ear.
SPEECH LANGUAGE PATHOLOGY & AUDIOLOGY HEARING DISORDERS OF THE OUTER EAR
Labelled Diagram of Inner Ear Inner Ear - Description The inner ear or labyrinth of the human ear comprises 2 structures - the bony labyrinth and the membranous labyrinth. Bony labyrinth is a series of cavities or channels present in the petrous part of the temporal bone. The membranous labyrinth is present within the bony labyrinth.

Inner Ear Problems Causes & Treatment of inner ear Dizziness & Vertigo
Inner ear: The inner ear, also called the labyrinth, operates the body's sense of balance and contains the hearing organ. A bony casing houses a complex system of membranous cells. The.
Common balance disorders Hearing Link
The inner ear is embedded within the petrous part of the temporal bone, anterolateral to the posterior cranial fossa, with the medial wall of the middle ear, the promontory, serving as its lateral wall.

Hearing Physics
Anatomy Function Associated Conditions Tests Essential for hearing and balance, each ear has an intricate structure of bones, nerves, and muscles. The ears can be affected by bacterial infections, viral infections, hearing loss, tinnitus (ringing in the ears), Meniere's disease, and more. Anatomy

Disorders of the Ear Part Two a PA Review and Podcast
inner ear, part of the ear that contains organs of the senses of hearing and equilibrium. The bony labyrinth, a cavity in the temporal bone, is divided into three sections: the vestibule, the semicircular canals, and the cochlea. Within the bony labyrinth is a membranous labyrinth, which is also divided into three parts: the semicircular ducts.